An In-depth Guide to Learning Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Learn the basics of AI & ML w/ this comprehensive guide. Covers math concepts, programming languages, tools & techniques. Includes resources & tips for staying current.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are among the most exciting and rapidly growing fields in technology today. From self-driving cars to personalized shopping recommendations, the applications of these technologies are vast and varied. But where do you start if you’re a beginner looking to learn about AI and ML? In this guide, we’ll take a look at a general roadmap for learning these cutting-edge technologies, and provide resources for learning each topic.
Start with the basics
The basics for learning Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) include a solid understanding of mathematical concepts, programming languages, and the tools and techniques used in these fields.
Mathematical Concepts
The mathematical concepts required for Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) include Linear Algebra, Calculus, Probability, and Statistics.
Linear Algebra: Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics that deals with vectors and matrices. It is used to represent and manipulate data in a high-dimensional space. In ML and AI, linear algebra is used to represent data in a compact form, perform matrix operations, and solve linear equations. Linear algebra concepts such as vector spaces, eigenvalues, and eigenvectors are used in ML to perform tasks such as dimensionality reduction and principal component analysis.
Khan Academy’s Linear Algebra course, MIT’s Linear Algebra course, and Gilbert Strang’s Linear Algebra textbook are all great resources for learning linear algebra.
Calculus: Calculus is the branch of mathematics that deals with rates of change and accumulation of quantities. It is used to optimize the parameters of a machine learning model. Calculus concepts such as gradient descent, partial derivatives, and optimization techniques are used in ML to minimize the error between the predicted and actual values of a model.
Khan Academy’s Calculus course, MIT’s Calculus course, and James Stewart’s Calculus textbook are all great resources for learning calculus.
Probability: Probability is the branch of mathematics that deals with random variables and the likelihood of events occurring. In ML and AI, probability is used to make inferences and predictions based on data. Probability concepts such as Bayes’ theorem, conditional probability, and random variables are used in ML to model uncertain systems and perform tasks such as classification, clustering, and anomaly detection.
Khan Academy’s Probability course, MIT’s Probability course, and Sheldon Ross’s Introduction to Probability Models textbook are all great resources for learning probability.
Statistics: Statistics is the branch of mathematics that deals with collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data. In ML and AI, statistics is used to model and analyze data, test hypotheses, and make decisions
Khan Academy’s Statistics course, MIT’s Statistics course, and David Freedman’s Statistics textbook are all great resources for learning statistics.
Programming Languages
Python is the most commonly used programming language in AI and ML. It has a large number of libraries and frameworks for machine learning such as Tensorflow, Pytorch, and scikit-learn. It also has a large community that contributes to the development of libraries and frameworks. Other popular languages include R and Julia.
Learning Python can be a great way to start your journey into the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) as it is widely used in these fields. Here are a few tips on how to learn Python:
Start with the basics: Learn the basic syntax and structure of the language. Get familiar with concepts such as variables, loops, and control structures. There are many online tutorials and resources, like Codecademy, that can help you get started.
Practice coding: Once you have a basic understanding of the language, practice coding by working on small projects. This will help you solidify your understanding of the concepts and become more comfortable with the syntax.
Learn the libraries: Python has a large number of libraries that can be used for different tasks. Some popular libraries for AI and ML include NumPy, pandas, and scikit-learn.
Work on real-world projects: Apply what you’ve learned by working on projects that are relevant to your interests. This will help you understand how to use Python in a practical context.
Join a community: Join a community of Python developers, such as a local meetup group or online forum. This will provide you with an opportunity to learn from more experienced developers and get feedback on your code.
Keep learning: Keep learning and exploring new features and libraries of Python as you progress. Python is a vast language and there is always something new to learn. Learn about advanced topics such as decorators, generators, and asyncio.
Take a course or a degree: You can also take a course or a degree in computer science or software engineering, which will cover Python as one of the main programming language and will provide you with a more comprehensive understanding of the language, its applications, and its ecosystem.
Read the documentation: The official Python documentation is a great resource for understanding the language and its features. The documentation is well-written and provides detailed explanations of the language and its libraries.
Remember, learning a programming language like Python takes time and practice. Be patient with yourself and don’t get discouraged if you encounter challenges along the way. The more you practice and learn, the more comfortable you will become with the language.
Here are five great resources for learning Python:
Codecademy: Codecademy offers interactive Python tutorials that are perfect for beginners. The platform is intuitive and easy to use, and the tutorials cover everything from basic syntax to advanced topics like object-oriented programming.
Coursera: Coursera is an online learning platform that offers a wide range of Python courses from top universities and institutions. The platform is great for self-paced learning, and many of the courses offer a certificate of completion.
Python.org: The official Python website is a great resource for learning the language. The website provides detailed documentation, tutorials, and examples to help you learn Python.
SoloLearn: SoloLearn offers a variety of interactive Python tutorials that are perfect for beginners. The app includes quizzes and coding challenges to help you practice and test your skills.
Learn Python the Hard Way: This book is a comprehensive guide to learning Python, and it’s great for beginners. The book covers the basics of the language and provides clear explanations and examples to help you understand the concepts.
These resources are great starting points for learning Python, but they are not exhaustive. There are many other resources available online and offline that you can use to supplement your learning. Additionally, taking a course or a degree in computer science or software engineering could provide you with a strong background in Python.
Tools and Techniques
Tools and techniques are the software and methodologies used to build and train machine learning models. These tools and techniques are essential for working with data, building and evaluating models, and deploying them in real-world applications. Some of the most common tools and techniques used in ML and AI include:
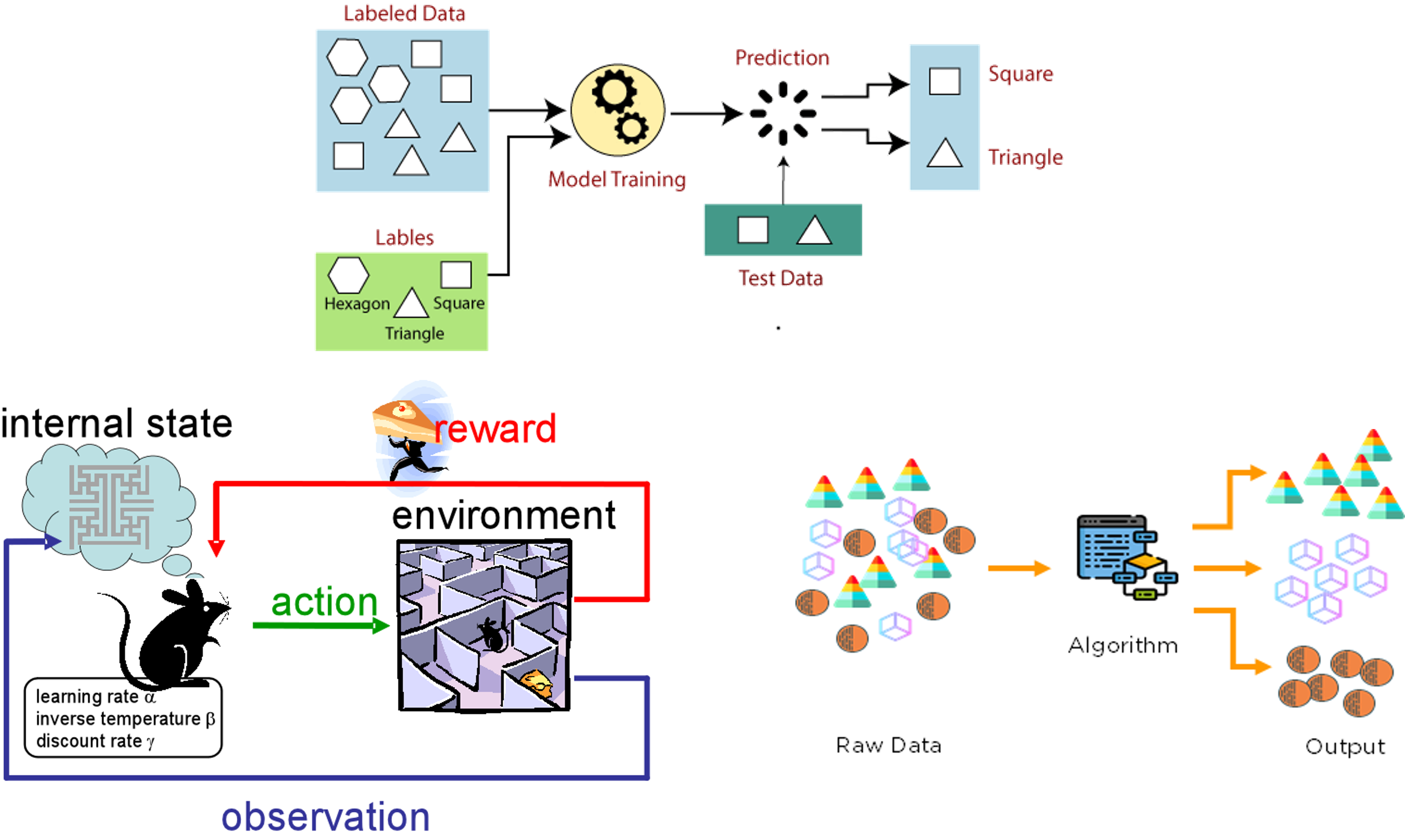
Supervised Learning: Supervised learning is the most common type of machine learning. It is used to train models to predict an output (label) from a given input (data). This type of learning is called “supervised” because the model is trained using labeled data (data with the correct output). Examples of supervised learning algorithms include linear regression, logistic regression, and support vector machines.
A more specific example of supervised learning is using a linear regression model to predict the price of a house based on its square footage, number of bedrooms, and location. The model is trained using labeled data (data with the correct output, the house prices), and can then be used to predict the price of a new house based on its square footage, number of bedrooms, and location.
Unsupervised Learning: Unsupervised learning is used to extract patterns or features from data without labeled output. This type of learning is called “unsupervised” because the model is trained using unlabeled data. Examples of unsupervised learning algorithms include k-means clustering, hierarchical clustering, and principal component analysis.
A more specific example of unsupervised learning is using k-means clustering to group customers into different segments based on their purchasing patterns. The model is trained using unlabeled data (data without the correct output, the customer segments) and can be used to discover patterns or insights in the data.
Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to behave in an environment by performing actions and receiving rewards. The agent learns to maximize the rewards over time by adjusting its behavior. This type of learning is used in applications such as game playing, robotics, and autonomous vehicles.
An example of reinforcement learning is training an agent to play a game such as chess by performing actions (moving the pieces) and receiving rewards (winning or losing the game). The agent learns to maximize the rewards over time by adjusting its behavior.
Neural Networks: Neural networks are a type of machine learning model that are inspired by the structure and function of the human brain. They are used to model complex patterns in data, and are particularly useful for image, speech, and natural language processing.
An example of using a neural network is using a convolutional neural network (CNN) to classify images of handwritten digits. The CNN is trained on labeled data (images of handwritten digits and their corresponding labels) and can then be used to classify new images of handwritten digits.
Deep Learning: Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers (deep) to model complex patterns in data. It has achieved state-of-the-art results in tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition. Popular deep learning frameworks include TensorFlow and PyTorch.
An example of deep learning is using a deep recurrent neural network (RNN) to generate natural language text. The RNN is trained on a large corpus of text data and can be used to generate new text that is similar in style and content to the training data.
Machine Learning libraries: There are many libraries available that provide pre-built machine learning models and functions, such as scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch, that make it easier to train and deploy machine learning models. These libraries also provide a wide range of tools and functionalities to help you preprocess data, evaluate models, and perform other tasks related to machine learning.
An example of using a machine learning library is using scikit-learn’s decision tree classifier to predict whether a customer will churn or not.
Data visualization tools: Data visualization tools such as matplotlib, seaborn, and plotly are used to visualize and explore data. These tools are useful for understanding the structure and patterns in data, which is important for building accurate and interpretable models.
An example of using data visualization tools is using matplotlib to create a scatter plot of the relationship between two variables in a dataset, such as the relationship between the price of a house and its square footage.
Cloud-based platforms: Cloud-based platforms such as AWS, GCP, and Azure offer a wide range of machine learning services and tools that make it easier to build, train, and deploy machine learning models. These platforms also provide access to powerful computing resources, making it possible to train large and complex models.
An example of using cloud-based platforms is using AWS SageMaker to train a machine learning model and then deploy it as an API that can be accessed from any application.
Data Science
Data science is an interdisciplinary field that combines statistical and computational methods to extract knowledge and insights from data. It is a growing field that is being used in many different industries to make data-driven decisions and predictions.
The process of data science typically involves several steps:
Data Collection: Data is collected from various sources such as databases, APIs, or sensors. The data can be structured or unstructured, and can be in the form of text, images, or numbers.
Data Cleaning: Data cleaning is the process of identifying and removing errors, inconsistencies, and missing values from the data. This step is important for ensuring that the data is accurate and usable.
Data Exploration: Data exploration is the process of analyzing the data to understand its structure, patterns, and relationships. This step is important for gaining insights into the data and identifying areas of interest.
Data Modeling: Data modeling is the process of building models to make predictions or inferences based on the data. This step is important for extracting knowledge and insights from the data.
Data Visualization: Data visualization is the process of creating visual representations of the data to make it easier to understand and communicate. This step is important for communicating the insights and predictions from the data to others.
Data Deployment: Data deployment is the process of putting the models into production and making them available to users. This step is important for making data-driven decisions and predictions in real-world applications.
Data science requires a combination of skills from computer science, statistics, and domain expertise. It is a rapidly growing field and has many applications in various industries such as finance, healthcare, retail, and transportation.
Get familiar with the libraries
There are many libraries available for Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) that provide pre-built models and functions to make it easier to train and deploy models. Here are a few examples of popular libraries:
TensorFlow: TensorFlow is an open-source library developed by Google for building and deploying machine learning models. It provides a wide range of tools for building, training, and deploying neural networks, and is particularly useful for deep learning tasks such as image and speech recognition.
PyTorch: PyTorch is an open-source library developed by Facebook for building and deploying machine learning models. It is similar to TensorFlow and is also commonly used for deep learning tasks.
scikit-learn: scikit-learn is an open-source library for building machine learning models in Python. It provides a wide range of pre-built models and functions for tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, and dimensionality reduction.
NumPy: NumPy is a library for working with arrays and matrices in Python. It is commonly used for numerical operations in machine learning and is a dependency for many other libraries such as scikit-learn and TensorFlow.
pandas: pandas is a library for working with data in Python. It provides functions for reading and manipulating data in a wide variety of formats and is commonly used in data cleaning and exploration tasks.
Keras: Keras is a high-level neural networks API, written in Python and can run on top of TensorFlow. It was developed with a focus on enabling fast experimentation and is a popular choice for building and deploying neural networks.
These libraries are constantly evolving and new libraries are being developed all the time. Keeping up with the latest advancements in the field and staying updated with the newest libraries and tools is important for staying current in the field of AI and ML.
Study machine learning algorithms
Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are mathematical models that can learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed. There are several types of ML algorithms, including:
Supervised Learning: Supervised learning algorithms are used to predict an output (label) from a given input (data). These algorithms are trained using labeled data, which means the data includes the correct output for each input. Examples of supervised learning algorithms include:
Linear Regression: Linear regression is used to predict a continuous output, such as the price of a house. It finds the line of best fit through the data points, and can be used for simple linear or multiple linear regression.
Logistic Regression: Logistic regression is used to predict a binary output, such as whether a customer will churn or not. It finds the best fit line through the data points and the output is a probability of the label (i.e. churn or not).
Support Vector Machines: Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are used for classification problems. It creates a boundary (hyperplane) between different classes in the data, and then new data points are classified based on which side of the boundary they fall on.
Unsupervised Learning: Unsupervised learning algorithms are used to extract patterns or features from data without labeled output. These algorithms are trained using unlabeled data, which means the data does not include the correct output for each input. Examples of unsupervised learning algorithms include:
K-Means Clustering: K-Means is a clustering algorithm used for grouping similar data points together. It finds k clusters in the data, where k is a user-defined parameter.
Hierarchical Clustering: Hierarchical clustering creates a hierarchy of clusters, where each cluster is divided into smaller clusters.
Principal Component Analysis (PCA): PCA is a dimensionality reduction algorithm used to reduce the number of features in a dataset while preserving as much information as possible.
Reinforcement Learning: Reinforcement learning algorithms are used to train agents to make decisions in an environment by performing actions and receiving rewards. These algorithms learn through trial and error and aim to maximize the total reward over time. Examples of reinforcement learning algorithms include: Q-Learning: Q-Learning is a type of reinforcement learning algorithm that uses a Q-table to store the expected reward for each action in a given state. The agent learns to take actions that lead to the highest expected reward.
SARSA: SARSA is a type of reinforcement learning algorithm that uses a Q-table to store the expected reward for each action in a given state. The agent learns to take actions that lead to the highest expected reward.
Policy Gradients: Policy Gradients methods are a family of reinforcement learning algorithms that optimize the parameters of a policy (a function that maps states to actions) directly. It uses gradient descent to adjust the policy to increase the expected reward.
These are some of the most popular machine learning algorithms, but there are many others that exist, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of algorithm will depend on the problem you are trying to solve, the type and amount of data you have, and the resources available for training and deploying the model.
Practice on real-world projects
The best way to learn is by doing, so apply what you’ve learned by working on projects such as image classification, natural language processing, and time series forecasting. Building your own projects will help you understand how to apply AI and ML to real-world problems.
Free resources: Kaggle (competitions and datasets), GitHub (open-source AI and ML projects)
Learn about the various applications of AI and ML in different fields such as medicine, finance, and autonomous vehicles. Understanding how these technologies are used in the real world will give you a better sense of their potential and limitations.
Free resources: Coursera (AI for Everyone, AI in Healthcare), edX (AI in Business, AI in Finance)
Stay current with the latest advancements
AI and ML are fast-moving fields, so it’s important to keep up-to-date with the latest advancements. Read research papers, follow the work of experts in the field, and attend conferences and meetups to stay current with the latest developments.
Free resources: arXiv (preprint research papers), AI conferences (ICML, NeurIPS), AI meetups
This is a general roadmap and you can customize it according to your needs and preferences. Also, it’s important to be patient and persistent, as learning AI and ML can take time and requires a lot of practice and hands-on experience. With the right resources and approach, you can unlock the full potential of these technologies and become proficient in AI and ML.